Nowadays, many businesses prefer to run their operations from a third-party facility since managing an in-house data center requires a lot of time, IT expertise, and a sizable budget. There are many factors for choosing a third-party facility, including:
- Much lower capital costs when compared to an in-house data center.
- Security & reliability. This is a top priority among data center providers. Features include 24/7 perimeter security, closed-circuit security monitoring and multiple layers of access control to the server room. In addition, they provide multiple backup and recovery options to keep services running during power outages and other unexpected events.
- Simpler management with little to no regular maintenance
- Higher levels of flexibility and scalability
- An opportunity to focus on other areas of the business such as IT improvements and innovation.
Although there are many advantages of colocation, benefiting from it depends on your ability to evaluate business needs and find the right partner.
Facility Location
When searching for a third-party location, you should consider the following primary location-related factors:
- Accessibility – ideally, the data center should be easily accessible to your IT staff. Trips to a distant location can be a problem for regular maintenance and emergencies, plus you will need to cover the trip expenses.
- Distance – The distance between your organization and the data center impacts Internet speed. This problem is not as notable with fiber wiring as these cables do not experience issues until the 25-mile mark. However, setting up in a facility a few states away from your customer base can cause problems.
- Power Grids – Find a data center that does not run on the same power grid as your business. That way, a regional power outage will not affect both the data and your company’s office.
- Latency – You may need a data center close to the source of your data generation to avoid latency issues.
- Disaster Recovery – Look for a data center in an area that is not prone to natural disasters (tornadoes, earthquakes, floods, tsunamis, etc.).
Although you could save money by signing up with a center that is further away, setting up your equipment in a nearby facility is typically a better business move.


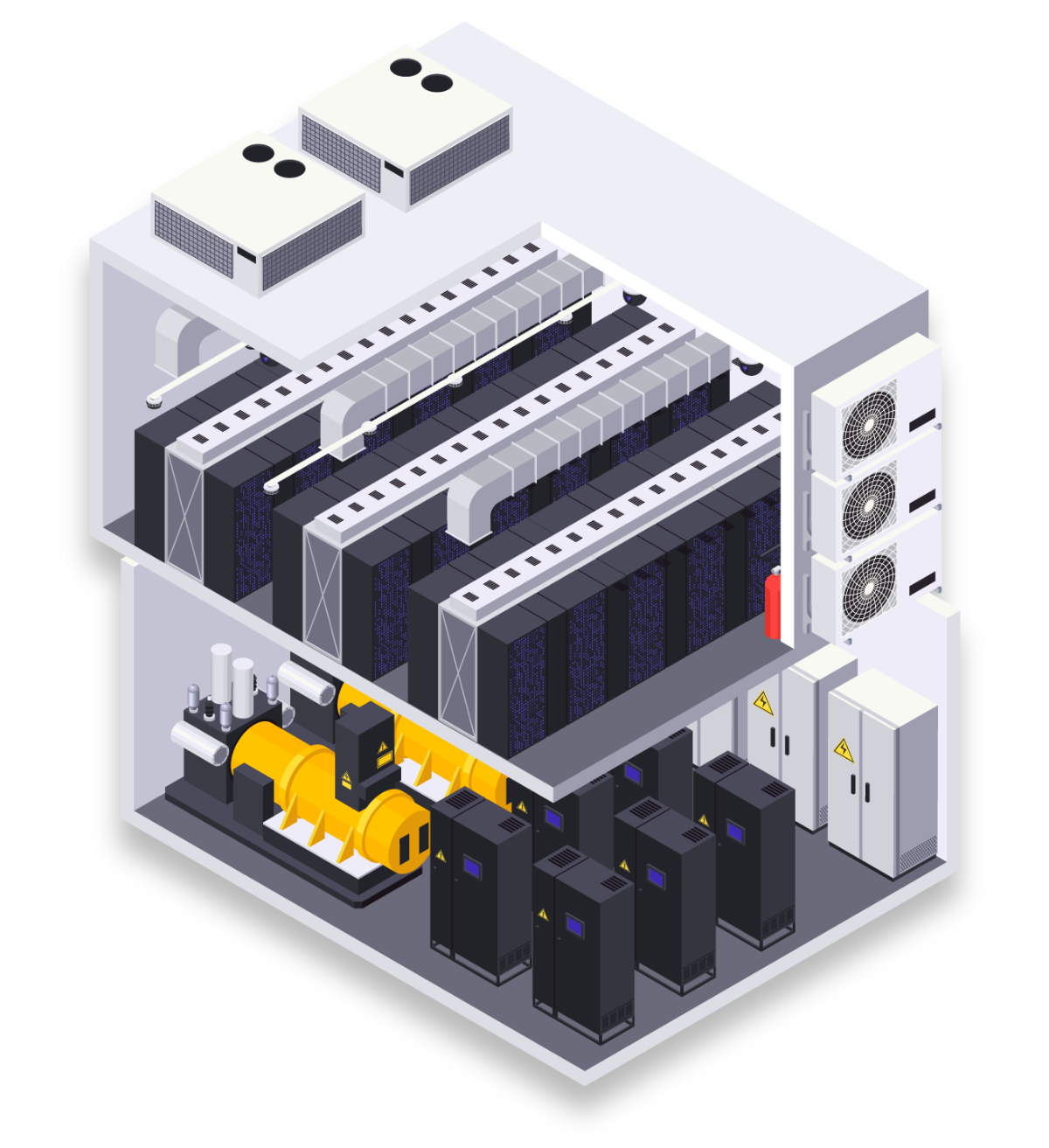
Data Center Infrastructure
Infrastructure in the data center includes physical and hardware-based resources including all IT devices, equipment, and technologies. Here are several key infrastructure factors when choosing a provider:
- The facility needs reliable MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems. The MEP includes electrical systems, cooling mechanisms, proper ventilation, fiber optic cabling, air handling systems, etc.
- A data center should have Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) to protect client’s setups from power failures, surges, and fluctuations.
- The data center should have high PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness). This metric is a ratio that describes how efficiently a facility uses power, which impacts your monthly bill and the overall stability of the facility.
- The facility should have connections to multiple power grids to ensure redundancy. In the event of a power shortage that takes out all grids, the data center should have batteries or flywheels.
- The center needs a proper fire suppression system and environmental controls.
- Since there is no governing body forcing businesses to keep their technology up to date, make sure your co-location facility is running the latest and greatest technology.
Choosing the wrong data center can lead to issues with connectivity, limited scaling, security breaches, and a ton of headaches. Use the factors we listed above to narrow the list of potential providers and find a co-location partner that meets all your IT and business requirements.


